Business Class
The hospitality sector is at an exciting crossroads, faced with a multi-faceted dynamic of changing consumer desires, fast-emerging technologies, and changed global business models. Housed in the past in physical goods like space and food, hospitality is increasingly defined by intangible concepts like personalized experiences, frictionless digital engagement, and changing demand for authenticity and sustainability. This shift sits atop every wish list in the industry, ranging from restaurateurs and hoteliers to policymakers and technology suppliers as they regroup their recipe for success during this new period. Its capacity to adapt to next-generation solutions in response to altered business conditions will decide its destiny for future triumph and to what extent it will be able to reconcile competing requirements of a growing, high-tech, and expanding more advanced and demanding global client base.
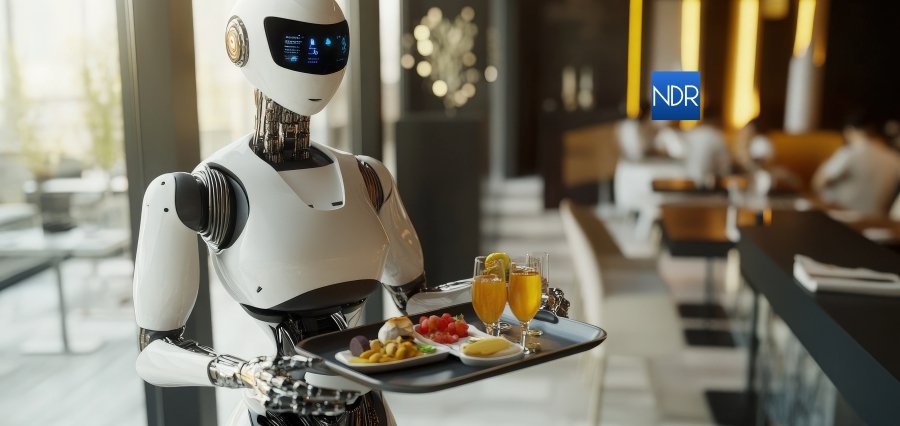
Technology’s uncontrolled pace is quite possibly the most attractive force driving hospitality transformation. From mobile check-in and smartphone to smart room technology and online booking systems, and from AI-powered customer service chatbots to digital concierge, technology is coming into contact with every element of the guest experience. Guests are now looking for instant information, frictionless digital interactions, and tech-facilitated personalized experiences. Hotel and hospitality companies are leveraging data analytics to find out about preferences of guests, customize offers, and predict requirements in advance. Internet of Things (IoT) is facilitating smart rooms through temperature and light control by guest preference, whereas virtual and augmented reality is creating pre-arrival experience with depth and more interaction on-site. All these technologies combined are not only convenience; it’s making the operations smarter, enhancing guest satisfaction, and bottom-line revenue increase in a nutty competitive virtual world.
This deployment is not however without difficulties. Hotel chains would be required to address data protection and privacy concerns, safeguarding the personal data of their guests. Additionally, there would be an increased requirement of experienced personnel trained to operate and utilize such advanced systems. Secondly, while technology can bring efficiency, the hospitality business can never compromise on human touch so integral to its value proposition. Trimming high-tech sophistication with genuine human touch is the biggest challenge for the new hospitality sector. Individuals still need personalized service and genuine connections, and technology will have to be employed to support, not substitute, these valuable elements of the hospitality equation.
The second driving force for hospitality is changing consumer expectations. Consumers and tourists are looking for more genuine, place-driven experiences rather than the usual tourist attractions. They desire to immerse themselves in the local culture, buy local, and be a responsible custodian. That authenticity drive is creating more and more boutique hotels, local eateries, and activities that honor what is unique about the destination. There is greater awareness also of being environmentally- and socially-aware as now there are more tourists in specific looking for nature-friendly hotels and environmentally-aware companies. Also fueling demand is the “bleisure” phenomenon where business travelers stay for extended periods of leisure as well, and hospitality operators’ work and leisure requirements are also required to be met. To address changing customer requirements, the hospitality sector is product diversification. Apart from traditional hotels, alternative accommodation in the form of boutique hotels and Airbnb is becoming trendy, with higher localization and more product variety. Restaurants have made farm-to-table a reality and accommodated different diets. Experiential best practices are also causing hospitality operators to become creative when it comes to out-of-the-box special activities and tours that allow guests to engage more with their destination. This transition to experience and customization is inviting hospitality players to become sensitive to indigenous cultures and develop products that are attuned to their values and choice of interested markets.
Global business trends also significantly influence hospitality. Economic activity cycles, geo-political forces, and pandemics all influence consumer travel and purchase patterns. The pandemic more recently, i.e., put in the limelight the industry’s exposure to third-party disruptions and the faster-than-expected adoption of contactless technology and the enhancement of hygiene measures. In the future, the hospitality sector must become more resilient by diversifying markets, keeping up with changing travel rules, and emphasizing guest and staff health and safety.Furthermore, international travel remains encouraged by globalization, compelling hospitality businesses to accommodate different diverse cultural tastes and needs.Sustainability is no longer a niche trend but a broader expectation among hospitality businesses. People are becoming increasingly aware of their carbon footprint and intentionally seeking companies with a history of sustainability. This is imposing hotels and restaurants to implement sustainable practices like waste reduction, energy and water conservation, sustainable material purchasing, and local conservation habits. Environmental program transparency and sustainability certification are increasingly becoming important to attract ecotourists. Incorporation of sustainability is not only a moral necessity but also a good business concept because it can result in cost savings, improved brand reputation, and improved customer loyalty.
Lastly, changing workforce trends are also transforming the hospitality industry. Employer attraction and retention in an increasingly competitive labor market is a top priority. The company is more concerned with making sure the working environment is a welcoming one, with fair wages and compensation, and career advancement. Usage of technology in reducing some of the operations is also stifling the labor shortage as well as streamlining. Empowering and educating the workers is required in providing the quality service the visitors require. Its prospects will depend not only on how it maintains its pace in the face of changing consumer desire and technological change but also on how it attracts, retains, and motivates highly competent and motivated employees.
By and large, the dynamic hospitality business is doing a creative dance between changing technology, changing consumer whims, international business models, increasing focus on sustainability, and changing workforce aspirations. To thrive and endure amidst this revolution period, hospitality businesses must innovate, personalize, take the mantle of truth, shock-proof, greenify, and invest in human beings. Anyone who can grasp these new paradigms will be well placed to decipher new possibilities and set the pace for this rapidly evolving and crucial industry’s future.
Read Also : The Role and Importance of Hotels in Driving the Regional Business